

What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a serious and advanced stage of gum disease (periodontal disease)

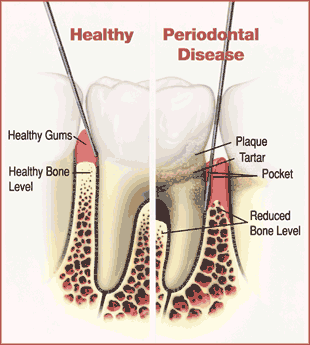
Periodontitis is a serious and advanced stage of gum disease (periodontal disease) that involves inflammation and infection of the gums and other structures supporting the teeth. It is characterized by the progressive loss of the bone around the teeth and the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums. Periodontitis is typically preceded by gingivitis, which is an earlier stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gums.
The main cause of periodontitis is the accumulation of dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. Plaque can harden into tartar (calculus) if not removed through regular oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing. The bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins that can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation.
As periodontitis progresses, the inflammation extends deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth, causing the breakdown of the bone and connective tissues that hold the teeth in place. This can result in tooth mobility and, if left untreated, eventual tooth loss.
Common signs and symptoms of periodontitis include:
-
Swollen and red gums.
-
Gums that bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing.
-
Persistent bad breath.
-
Receding gums, making teeth appear longer.
-
Formation of deep pockets between the teeth and gums.
-
Changes in the way teeth fit together when biting.
Periodontitis can have systemic implications, as it has been associated with various health conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory problems. Therefore, early detection and prompt treatment of periodontitis are essential to prevent further damage to the oral structures and potential systemic health issues.
Treatment for periodontitis may involve professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar, and, in severe cases, surgical procedures to address the damaged tissues. Good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups are crucial for preventing and managing periodontitis. If you suspect you may have gum disease, it's important to consult with a dentist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
what should i do with Periodontitis?
If you suspect that you have periodontitis or have been diagnosed with the condition, it's important to take prompt action to manage and treat it. Here are steps you can take:
Consult a Dentist:
-
Schedule an appointment with a dentist or periodontist for a thorough examination and diagnosis. A dental professional will assess the severity of the periodontitis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Professional Dental Cleanings:
-
Undergo professional dental cleanings, which may include scaling and root planing. These procedures help remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and below the gumline.
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
-
Adopt a rigorous oral hygiene routine at home. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, and make sure to clean between your teeth using dental floss or interdental brushes. Proper oral hygiene is crucial for managing and preventing the progression of periodontitis.
Antibacterial Mouthwash:
-
Your dentist may recommend an antibacterial mouthwash to help control the bacterial load in your mouth. This can be an adjunct to your regular oral hygiene routine.
Quit Smoking:
-
If you smoke, consider quitting. Smoking is a significant risk factor for periodontal disease, and quitting can improve the success of treatment.
Address Contributing Factors:
-
Address any underlying factors that may contribute to periodontitis, such as poorly controlled diabetes. Managing systemic conditions can positively impact your oral health.
Follow-up Appointments:
-
Attend regular follow-up appointments with your dentist or periodontist. Periodontitis requires ongoing monitoring and management to ensure its control and to address any flare-ups.
Consider Lifestyle Changes:
-
Evaluate and make lifestyle changes that promote overall health, as systemic health can impact oral health. This may include maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and staying physically active.
Surgical Interventions (if necessary):
-
In advanced cases, surgical interventions such as periodontal surgery or gum grafts may be recommended to repair damaged tissues and restore gum health.
Remember that early detection and intervention are key to managing periodontitis effectively. Ignoring the condition or delaying treatment can lead to more severe complications, including tooth loss and potential impacts on systemic health.
Always follow your dentist's recommendations and maintain regular dental check-ups to monitor the progress of treatment and address any emerging issues promptly. If you have concerns about your oral health, consult with a dental professional for personalized advice and care.

